
Milk samples will be aseptically collected using standard procedures. Additional milk cultures will be taken on does with clinical mastitis or with SCC exceeding 800,000/ml at any monthly test. Goats will be tested for CAEV and milk cultured for bacteria for intramammary infection (IMI) at enrollment (freshening), mid-lactation (150 days in milk) and the end of lactation. Goats with clinically enlarged joints (as determined by the investigator) will be excluded from the study. DHIA records will be reviewed on a monthly basis for change in SCC and to record 305-day milk yieldĪnd composition data. Breed, parity, kidding group (month) and prior mastitis history will be recorded. Serum ELISA test for CAEV antibody and PCR of peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) for CAEV pro-viral DNA (as previously described) will be used to determine infection status at enrollment and to categorize goats as uninfected, infected during the study period,or infected throughout the study period. We expect an 8-month enrollment period (starting at beginning of fall kidding) and 10 month follow-up per animal.
Animals will be pre-screened for enrollment as they approach kidding due date. Herd management can further reduce the exposure of susceptible goats to the virus.Project Methods CAEV-infected does (n=140), as determined by positive serum CAEV-ELISA and PBMC CAEV-PCR,without signs of joint enlargement (sign of clinical CAEV infection) and CAEV-uninfected does (n=160), as determined by negative CAEV-ELISA and PBMC CAEV-PCR tests) will be will be enrolled at time of freshening. If practised, in conjunction with test and culling of serological positive goats, owners can reduce the level of infection on a property over time. Promote hygienic management of the kids to avoid contamination by CAE from birth until maturity. If you lend or agist your goats and intend for these animals to return to your property, make sure you assess the CAE risk of the property where they are going before sending them and remember people and objects such as grooming tools, feed bins, rugs and trailers can transfer CAE from one property and herd to another. Insist on a fully completed and signed National Goat Health Statement from the seller. No goat should be tested within one month of any vaccination. Adult does should not be tested in the period from one month either side of kidding as inconsistent results could occur. Repeated blood testing during a 12-month period will detect the majority of infected goats (a very small number may take longer to detect). Testing should be performed on goats six months and older. The best way to know if your herd has CAE is to have all animals over six months of age blood tested, this can be done by one of our veterinarians.

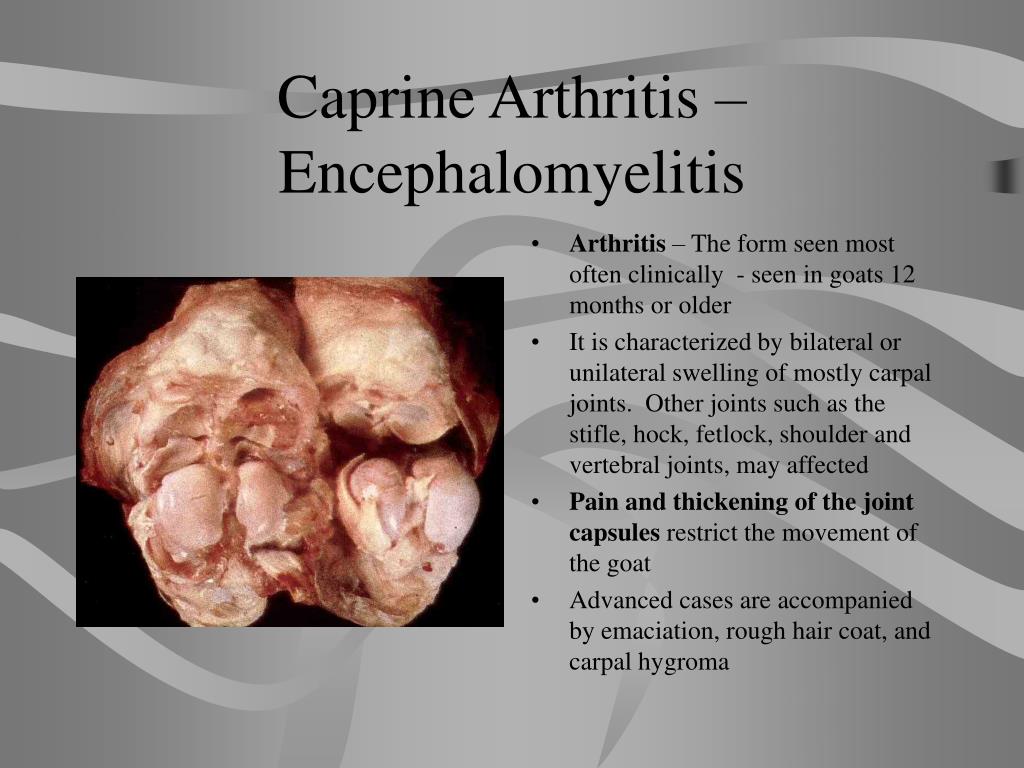
(Kids less than six months of age are more likely to show neurological disease)Ĭlinical signs can appear in an infected goat if the goat is exposed to stressful situations such as poor nutrition and overcrowding, which means well managed infected goats may never show clinical signs. Neurological symptoms leading to progressive paralysis.Arthritis in any joints, most notably the carpal joints (big knee).The signs of CAE are mainly due to the body’s reaction against the infected cells. Symptoms can vary markedly between animals, with most well managed goats showing no obvious clinical signs.

People may also contribute to the spread of infection with contaminated hands, clothing, equipment and footwear.Ī clean goat herd will most likely become infected by a CAE-positive goat coming on to the property. Transfer sometimes occurs by blood on gear such as vaccination needles, tattooing equipment, dehorners and foot/fibre shears, or through exposure to open wounds. Goats kept in close quarters can spread the virus through respiratory secretions, eg nasal discharge, and cough, saliva and tears.

However, there is a risk of spread during the birth process if the kid is contaminated with blood due to vaginal tears. The virus does not cross the placenta and kids born to infected does generally, do not always have the disease. The main spread of the virus between goats is through drinking infected milk either as a kid or as an adult. The disease is also known as ‘big knee’ and is caused by a lentivirus or ‘slow’ virus associated with encephalomyelitis in kids and slowly-developing disease syndromes in older goats. CAE is also considered an animal welfare issue. Caprine Arthritis Encephalitis is a serious disease that causes mastitis, ill-thrift, arthritis, pneumonia, and paralysis that moves up the body, and brain disease (encephalomyelitis).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
